The Varilux progressive lens was first introduced by Bernard Maitenaz in 1959,enabling clear distance vision on upgaze versus reading vision and in between on downgaze.
The post Can you get rid of Reading Glasses? appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>
Why would you want to? Lightweight tailor-made options exist.
Most people need reading glasses or accept sub-optimal results. Refractive surgery often claims to “throw away your glasses, and sometimes this results but usually with some trade-offs between each eye, pupil sizes and ranges of focus.
The Varilux progressive lens was first introduced by Bernard Maitenaz in 1959, enabling clear distance vision on upgaze versus reading vision and in between on downgaze.
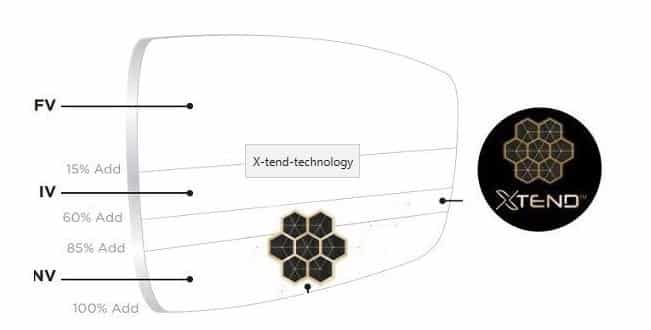
The Varilux X lens (an 8th generation lens) was designed as Generation X use their entire near space to carry out multiple activities, often digitally based with near vision up to arm’s length.
Xtend technology (a patented innovation) curbs vertical and horizontal variations in power to maximize field depth and expand the field of vision, minimising aberrations and maximising visual acuity.
Nanoptix elements are managed through clusters of seven elements to combine their power and multiply their effects for the maximum 3-dimensional “volume of acuity” needed for comfortable vision.
The best designs deliver an enlarged volume of vision is considerably enlarged both in width and depth.
The Xtend technology delivers visual acuity at a higher level than the threshold previously defined (0.15 Log MAR at 70 cm)
The Varilux X series was tested on a large group of wearers before commercialized, including personalising the progressive lens design according to the wearer’s needs and their individual body, head and gaze dynamics, and eye posture habits.
The amount of lowering of the gaze, fixations and saccades employed are individually recorded for the maximum visual acuity.
Specialists such as ergonomists, physiologists, sociologists and optics designers in a test house containing Essilor’s Movis Laboratory infrared cameras were used to capture wearers’ posture and movements using their lenses for different acuity demands in the vital area up to 70 cm –the so-called arm’s-length vision where the added power is about 70%.
Essilor’s research teams developed a special vision task that can be performed without correction(uncorrected ametropia ranging from -10.00D to +7.50D in near-vision power) to reflect the wearer’s reading posture.
This so-called pseudo-reading consists of observing and tracking a large-size object – i.e. one that does not require visual acuity. The object is blue against a white background and shown on a tablet. The movement of this target across the screen is similar to the average reading behaviour of an adult,
The downward gaze angle, the lateral offset, and the reading distance – describe the wearer’s posture, which is ultimately measured by the average posture during the pseudo-reading task and is called the NVB Point.
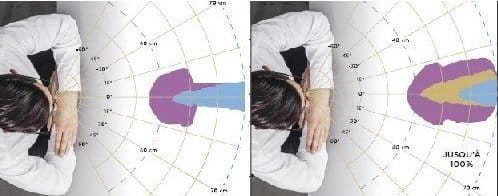
The wearer’s NVB Ratio describes how the wearer adjusts his or her gaze vertically during the entire measurement. The various colours indicate the different levels of acuity to perform typical tasks at each distance.
That ratio is close to 0 for wearers who have a strong tendency to lower their eyes whenever they move to the next line, and therefore change their head and body posture or the tablet position only slightly; the ratio is close to 1 when wearers maintain a static gaze position, i.e., they have a strong tendency to change their posture and/or the tablet position vertically while reading.one end of the scale is 0 for people who tend to lower their eyes as they scan down a piece of near work and at the other end 1 is for someone who tends to lower their head keeping their eyes still when they scan. The ratio is everything in between e.g. someone who only lowers their eyes 90% and the other 10% is with their head will have a ratio of 0.1 and so on.
The NVB ratio overall has two parts:
• the postural data – working distance; downgaze and lateral offset which work primarily on the position of the “eXtend ” area (near / intermediate within the zone 40 – 70cm) and
• the behavioural data – which works primarily on the size of the Xtend area
However, the two work together to locate the zone for the individual wearer.
READ MORE ABOUT NEAR VISION BEHAVIOUR
Method for Measuring Near-Vision Behavior (NVB)
1) The wearer’s frame is positioned in a clip that is used to define the frame’s position in space and, by extension, the wearer’s posture and head movements
2) The wearer’s baseline far-vision position is measured in primary gaze position, using the Visioffice 2
3) The wearer grasps the tablet and gazes at the blue dot in the centre until detected by the camera; then, the movement of the target is activated, and the gaze position and movements are continuously recorded
The data records
- The NVB Point, which is the wearer’s average gaze position during the measurement, representing the wearer’s reading posture;
- The NVB Ratio distributes measurements around the NVB Point and represents the wearer’s dynamic near-vision behaviour.
X = NVB Posture
Y = NVB Behavior
Wearers data involves prescriptions, interpupillary distance, the position of the eye’s centre of rotation) and the conditions in which the lenses are worn (shape and size of the frame, lens-eye distance, pantoscopic tilt, and wrap angle) combined with the characteristics of the lenses to be produced (front and back surface design, geometry and refractive index).
The optimal position of the near-vision zone on the progressive lens is based on the wearer’s posture (as indicated by the NVB Point). Information on ametropia, prismatic effects, and binocular vision is taken into account during this stage.
The progression profile based on the wearer’s gaze dynamics, i.e. NVB Ratio, to ensure the optimum size and shape of the progressive lens zones.
The exact values for progression length and inset for the near-vision zone are arrived at by advanced calculations.
Essilor’s Research & Development mapped a graph of possible behaviours - the horizontal axis shows the wearer’s average posture while reading, expressed as a downward gaze angle (from
12 to 30 degrees); - the vertical axis shows near-vision behaviour, i.e., the dispersion of the gaze direction (between 0 and 1).
Thus, a wearer who adopts a sharp downward gaze while reading and primarily uses his eyes to explore his near- vision vertically will fall at the bottom-right portion of the graph. By contrast, a wearer who lowers eyes only slightly to read and primarily changes posture or moves the tablet while reading will fall at the upper left of the graph. Every kind of behaviour between these two extremes can be located on the graph.
Moreover, this mapping process includes a colour code; there is a significant effect on the optical design of the lens only if the eye can differentiate the colour codes for the two measurements. This offers an immediate way to verify that the measurements are reproducible.
Thanks to large wearer studies, each wearer’s behaviour is reproducible and represents an appropriate datapoint for customization since it is specific to each individual and differentiating.
• Near-Vision Behavior (NVB) personalization aims to ensure lenses are designed and tailored as closely as possible to the wearer’s specific posture and behaviour during near vision work.
• NVB technology is the perfect complementary feature to the Varilux X series lenses, providing the ultimate personalization tailored to the wearer’s needs.
• The process involves two phases: first, the individual’s postural behaviour must be measured and analyzed; second, a personalized design must be computed.
The post Can you get rid of Reading Glasses? appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>