
WHAT IS A MIGRAINE?
Migraine headaches, sometimes preceded by warning symptoms, can have specific triggers but also can vary in severity and type.
As distinct from the tight band type tension headache and the cluster headache often around one eye, the classic migraine is on one side of the head with the vision effected. Migraine is a common headache disorder with no conclusive cures, of many types affecting about 15 per cent of the population, but much is underdiagnosed and can have serious health risk warnings eg women suffering from migraine with aura at any age should never use oral contraceptives accordingly.
A diagnosis of migraine is one of exclusion. especially in recent onset cases, increasing severity/frequency, neurological symptoms of pins and needles and visual field defects all indicate further work up is indicated eg MRI with a neurologist or neuro-ophthalmologist
Migraine can be triggered by many factors such as food, medication,weather, stress, lack of sleep, skipping meals, dehydration. Triggers need to be kept in a diary,ideally.
WHAT CAUSES MIGRAINES ?

WHAT CAUSES MIGRAINE PAIN ?
Researchers have identified more than 20 irregular chromosome segments associated with migraine. Each potential genetic error affects how nerve cells work in a different way. The most effective treatments control the individuals triggers for migraines often called predisposing and precipitaing factors.
The brainstem is a complex intersection of nervous system wiring at the base of our brain in clusters of cell bodies called nuclei. From these nuclei, new signals are rerouted to other parts of the brainstem and the rest of the brain.These nuclei control pain, stress, balance, mood, sleep and the autonomic nervous system.
MEDICAL FILTERS
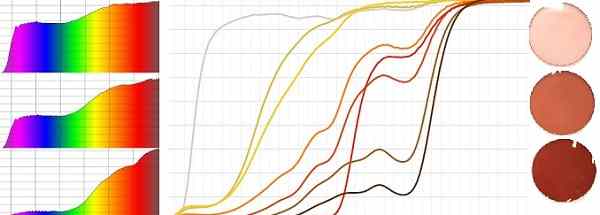
The FL-41 tint has been used successfully for migraine sufferers and in certain neurological conditions.
READ MORE
At 75% luminous transmittance or 25% absorption as an over the counter sunglass category 2 (43% to 80% luminous transmittance) it would have to be marked
“Not suitable for driving at twilight or night” or “Not suitable for drivng at night or under conditions of dull light”
Traffic signal visibility requirement must also be met for OTC and prescription. If they don’t then they must be marked “Notsuitable for driving and road use”
If they are considered precription, then AS/NZS ISO 8980-3 applies,
6.3.4 Driving in twilight or at night refers spectacle lenses with a luminous transmittance less than 75% shall not be used for driving in twilight or at night.
Medical filters are dyed according to the transmission curve
MEDICAL FILTER LENSES can be used for
• Age-related macular degeneration
• Albinism
• Diabetic retinopathy
• Retinitis pigmentosa
• Achromatopsia (colour blindness) Migraines
• Cone-rod-dystrophy
• Iris coloboma
• UV protection for pseudophakia and aphakia
• Photochemotherapy,
Medical filter lenses absorb short-wave blue light components more strongly than conventional sun protection lenses or contrast-enhancing lenses. Medical filters lenses can restrict peripheral vision due to the (almost) complete absorption of short-wave blue and violet light – which is extremely important in sports.
The short-wave violet and blue light causes scattering in the eye, which leads to glare and a reduction in acuteness of vision.
The contrast is increased by the difference between the strongly and less strongly exposed receptors.
Visual symptoms such as blurred vision, visual aura and photophobia can occur during migraine attacks, but not necessarily always.
Less than half of current migraine sufferers have been formally diagnosed, and about one-third are thought to receive appropriate treatment with prescription medications.
Colourimeter research data determines certain specific tints can help migraine sufferers whose migraines are triggered by pattern glare.
BPI manufactures the pink FL-41 dye is a mixture of colours that blocks the blue-green wavelengths.
BPI is the world’s largest manufacturer of optical tints.
Though the efficacy of Blue Light Blockers can vary, environmental exposure to blue light, including those from digital screen technology, does not cause significant damage to eyesight. Therefore, filtering out the blue light from screens is not essential but can be helpful.
The FL-41 tints in 25, 50 and 75% transmissions. (The % related to how dark the tint saturation is.) are sometimes prescribed for patients with migraine or brain trauma.
Research shows that there is not one specific colour to treat migraine (or any condition) as peoples vision and brains react differently and need to be treated individually. This is the reason the Colorimeter has 110,000 different colour combinations.
Pattern glare tests involve tints (that later can be prescribed) often but not always blue or yellow to reduce nausea that can arise from stripe patterns for some people by reducing or changing the contrast between black and white.
The theory is some people have a hyperactivity imbalance between their central and peripheral vision for light, flicker and specific spatial frequencies in stripes and patterns and can make reading difficult.
Optometrists do not treat “dyslexia” or even learning difficulties, but learning-related vision problems, and in the above cases treat people with pattern glare with tints when it affects reading.
Migraine is a complex and the most common neurological condition and classified by the World Health Organisation as the 7th most disabling disease worldwide, the 4th for women. It is three times more common in women than it is in men and is usually inherited. It is a very individual condition. Some people experience only an odd attack, while others suffer them regularly
TYPES OF MIGRAINES
RETINAL MIGRAINE
A retinal migraine (aka ophthalmic, migraine, visual, ocular ) has the temporary loss of vision effect by definition. (A headache that lasts from 4 -72 hours.)
An aura usually appears in both eyes.
Retinal migraines involve episodes of temporary vision loss or blindness in one eye only.
A retinal migraine often comes on suddenly in concert with head pain and nausea from a vascular spasm in or behind an eye.
Retinal migraines are apparent in 1 in 200 migraine sufferers with short-term loss of vision in one eye only.
• flashing lights or haloes
• blind spots in your field of vision
• partial or complete blindness
• affect one side of the head
•painful
• aggravated by activity
• nausea and vomiting
• sensitivity to light/sound
MIGRAINE WITH AURA
Aura :
Blind spots
Flashing lights
Zig-zag patterns
Pins and needles on one side usually starting in the fingers/ arm, sometimes spreading up into the face.
Slurring of speech
Muscular weakness
Loss of co-ordination
Confusion) up to an hour duration can occur in about 20% of cases before the actual headache.
The actual headache:
Intense throbbing headache, usually on one side of the head, worsened by movement and lasting from 4-72 hours.
Nausea, sometimes vomiting.
Sensitivity to light, noise, smells, Stiffness of the neck and shoulders, Blurred vision.
MIGRAINE WITHOUT AURA
Most commonly, migraine occurs without the aura but with the headache
The intense throbbing headache, usually on one side of the head, worsened by movement and lasting from 4-72 hours.
Nausea, sometimes vomiting
Sensitivity to light, noise, smells
Stiffness of the neck and shoulders.
Blurred vision
MIGRAINE WITHOUT HEADACHE
Occasionally migraineurs can experience only the aura of
Blind spots
Flashing lights
Zig-zag patterns
Pins and needles on one side usually starting in the fingers/ arm, sometimes spreading up into the face.
Slurring of speech
Muscular weakness
Loss of co-ordination
Confusion
OPTHALMOPLEGIC
As well as the headache occurring mainly in young people, there is the weakness of one or more of the muscles that move the eye, dilate the pupil and control the eyelids.
BASILAR
Rarely in young women, mainly loss of balance, double vision, blurred vision, difficulty in speaking and fainting.
Headache, loss of consciousness. Basilar migraine occurs when the circulation in the back of the brain or neck is affected.
HEMIPLEGIC
It is rarely headache but with temporary numbness, weakness, or even paralysis on one side of their body up to a few days in duration.
MRIs, CT scans and other neurological tests are required to rule out stroke, blood clot stroke, pituitary tumour, detached retina, or drug abuse.
Treatment causes etc
Acute medications used include the normal NSAIDs such as Ibuprofen,anti-nausea medication as well as preventative medications.
VESTIBULAR
Many migraine sufferers experience some vestibular symptoms during their lifetime, such as dizziness, sensitivity to light/sound and stiffness of the neck
but severe vestibular migraine can encompass
Severe dizziness
Vertigo
Sensitivity to light, sound, smell
Nausea and vomiting
Ataxia (loss of control over bodily movement)
Neck pain
Muscle spasms in the upper spine area
Confusion
At 75% luminous transmittance or 25% absorption as an over the counter sunglass category 2 (43% to 80% luminous transmittance) it would have to be marked
“Not suitable for driving at twilight or night” or “Not suitable for drivng at night or under conditions of dull light”
Traffic signal visibility requirement must also be met for OTC and prescription. If they don’t then they must be marked “Notsuitable for driving and road use”
If they are considered precription, then AS/NZS ISO 8980-3 applies,
6.3.4 Driving in twilight or at night refers spectacle lenses with a luminous transmittance less than 75% shall not be used for driving in twilight or at night.
Medical filters are dyed according to the transmission curve
MEDICAL FILTER LENSES can be used for
• Age-related macular degeneration
• Albinism
• Diabetic retinopathy
• Retinitis pigmentosa
• Achromatopsia (colour blindness) Migraines
• Cone-rod-dystrophy
• Iris coloboma
• UV protection for pseudophakia and aphakia
• Photochemotherapy,
Medical filter lenses absorb short-wave blue light components more strongly than conventional sun protection lenses or contrast-enhancing lenses. Medical filters lenses can restrict peripheral vision due to the (almost) complete absorption of short-wave blue and violet light – which is extremely important in sports.
The short-wave violet and blue light causes scattering in the eye, which leads to glare and a reduction in acuteness of vision.
The contrast is increased by the difference between the strongly and less strongly exposed receptors.
Visual symptoms such as blurred vision, visual aura and photophobia can occur during migraine attacks, but not necessarily always.
Less than half of current migraine sufferers have been formally diagnosed, and about one-third are thought to receive appropriate treatment with prescription medications.
Colourimeter research data determines certain specific tints can help migraine sufferers whose migraines are triggered by pattern glare.
BPI manufactures the pink FL-41 dye is a mixture of colours that blocks the blue-green wavelengths.
BPI is the world’s largest manufacturer of optical tints.
Though the efficacy of Blue Light Blockers can vary, environmental exposure to blue light, including those from digital screen technology, does not cause significant damage to eyesight. Therefore, filtering out the blue light from screens is not essential but can be helpful.
The FL-41 tints in 25, 50 and 75% transmissions. (The % related to how dark the tint saturation is.) are sometimes prescribed for patients with migraine or brain trauma.
Research shows that there is not one specific colour to treat migraine (or any condition) as peoples vision and brains react differently and need to be treated individually. This is the reason the Colorimeter has 110,000 different colour combinations.
Pattern glare tests involve tints (that later can be prescribed) often but not always blue or yellow to reduce nausea that can arise from stripe patterns for some people by reducing or changing the contrast between black and white.
The theory is some people have a hyperactivity imbalance between their central and peripheral vision for light, flicker and specific spatial frequencies in stripes and patterns and can make reading difficult.
Optometrists do not treat “dyslexia” or even learning difficulties, but learning-related vision problems, and in the above cases treat people with pattern glare with tints when it affects reading.
Migraine is a complex and the most common neurological condition and classified by the World Health Organisation as the 7th most disabling disease worldwide, the 4th for women. It is three times more common in women than it is in men and is usually inherited. It is a very individual condition. Some people experience only an odd attack, while others suffer them regularly
