Glaucoma Cataracts Diabetes
Glaucoma Cataracts Diabetes
Peter D’Arcy Optometrist Bega monitors such conditions utilising where necessary Canon OCT (optical coherence tomography) to aid in evaluation ensuring the maximum vision is preserved and corrected. The latest Canon OCT allows for high-resolution evaluation of eye anatomy eg high definition cross-sectional and three-dimensional images to determine the extent of complications.
Your eyetest for glaucoma

A family history of glaucoma, high eye pressure
Age over 50
African or Asian descended ethnicity
Diabetes, Short or long-sightedness
Previous history of eye injury
Past or present prolonged use of cortisone drugs
Migraine
High or low blood pressure
READ MORE ABOUT GLAUCOMA
Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. Half of the people with this condition in Australia are undiagnosed. There may be no warning symptoms.
More than 95% is undiagnosed in developing countries. Early detection and adherence to treatment are vital.
Glaucoma is a complex disease, Family history is vital.
Genetic testing is being developed as over 100 genes cause glaucoma.
Over 40 per cent of people have a positive family history. Many systemic and ocular conditions can be associated. Glaucoma Australia promotes the risk awareness campaign for developing glaucoma affecting over 300,000 Australians to encourage regular eye testing. The prevalence of diabetes and glaucoma is climbing rapidly. Serious complications include diabetic eye disease.
We can monitor Visual fields by Medmont computerised perimetry.
We can assess vision and any vision loss and monitor for referral, including cataracts.
While anyone may develop glaucoma, if you have a first degree relative with glaucoma, you have a 1 in 4 chance of developing glaucoma as well.
Over 40 per cent of people have a first-degree relative (parent, brother or sister) affected by glaucoma. Iritis can be painful, but closed-angle glaucoma would be the most painful. The vision would be reduced, unlike in conjunctivitis.
By studying the drainage angles, the risk of angle-closure can be made. It can result in a hazy cornea from oedema. Oral Diamox 500 mg and pilocarpine drops can temporarily reduce the eye pressure if the diagnosis is confirmed and surgical drainage solutions may be required. Ideal glaucoma treatments include eye drops inserted into the inner corner of the eyelids with punctal occlusion. Although there is evidence that cannabis lowers intraocular pressure, its role as a viable glaucoma therapy is limited by a short duration of action, psychotropic effects, and possible tachyphylaxis. Cannabis is a genus of plant best known for producing a family of compounds known as ‘cannabinoids. Over 60 different cannabinoids occur naturally, but only a handful have been researched in detail.
OCT scan | Ocular Coherence Tomography
Laser light from the red end of the visible spectrum (close to infra-red) is bounced back in different directions and manifests as an ultra-accurate map of the anatomical structures. The Canon OCT has 3 μm optical axial resolution 70,000 A scan/second allowing for accurate 10 layer segmentation, comparison and progression. It is non-invasive and non-contact. While nine out of 10 Australians say that sight is their most valued sense, over 8 million Australians are still not having regular eye tests though recommended.
Your eye test for cataract
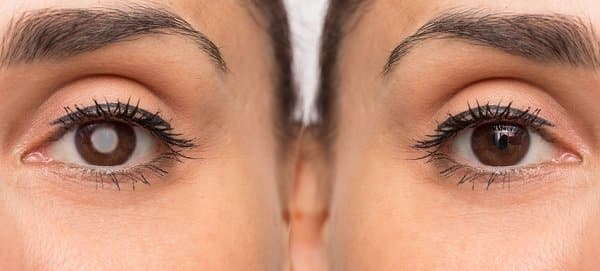
A referral can be recommended for cataract surgery at the appropriate time for cataract removal. Cataracts are very common in the long term with advancing age but can be present at birth or later as a result of metabolic conditions, medications, exposure to radiation, electric shock, trauma, and ocular or systemic diseases. Such clouding of all or part of the lens may affect sight differently in bright light or dim light as the pupil will be a different size. Cataracts are a leading cause of blindness and the treatment of cataracts is the most common eye surgery performed.
Read more about cataracts
A cataract is a clouding of the transparent tissue behind the iris that occurs in so-called age-related cataracts. Types of cataracts are graded by density and location during eye examinations during the early stages to ensure the risk of cataracts, and other eye conditions do not degrade vision. A nuclear cataract forms deep in the lens’s central zone (nucleus). Nuclear cataracts usually are associated with aging. A subcapsular cataract occurs at the back of the lens and is often associated with diabetes or steroid medications. Cortical cataracts tend to develop from the periphery towards the centre. They can be caused from:
Excessive exposure to UV to the lens of the eye
Omitting to wear sunglasses which can prevent cataract.
Smoking.
Obesity.
High blood pressure.
Previous eye injury or inflammation.
Previous eye surgery.
Protein clumping within the lens
Signs and symptoms
Frequent changes in spectacle or contact lens prescription
Clouded, blurred, distorted or dull vision.
Poor contrast sensitivity.
Increasing difficulty with vision at night
Sensitivity to light and glare
Need for brighter light for reading and other activities
Seeing “halos” around lights
Fading or yellowing of colours or colour deficiency.

Cataract type can vary from Nuclear, Posterior sub capsule, Morgagnian(A Morgagnian cataract arises when a cortical cataract becomes hypermature. ) (Pseudo exfoliation can sometimes be present with glaucoma.)Normal, Immature, Mature Hypermature, Cortical
IOL (Intraocular lens) designs can vary as well.

Cataract removal surgery normally involves replacing the cloudy lens with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL).
The decision is often based on visual acuity and other functional vision factors.
The natural lens is broken up by phacoemulsification where the pieces are removed via a tiny incision of the cornea. The IOL is then inserted through the incision and unfurls into the lens capsule. The incisions and cataract opening and division are performed usually by a surgical laser.
The clear lens protein of the eye can degrade over time often because of cumulative UV causing a cataract. Animal studies are being used to test preventative medications so as not to increase the risk of cataract.
Some inherited genetic disorders, age, cumulative exposure to UV can increase your risk of developing cataracts. Cataracts can also be caused by past eye surgery or medical conditions such as diabetes.
READ MORE ABOUT THE ADVANTAGES OF FEMTOSECOND CATARACT LASER SURGERY
Traditional cataract surgery uses a metal or diamond blade to perform the procedure with phacoemulsification (ultrasound waves) to break up and remove the cataractous lens, but laser-assisted (bladeless) cataract surgery uses a femtosecond laser that emits short pulses and allows precise laser incisions (even allowing correction of astigmatism from an irregularly shaped cornea). Traditional cataract surgery utilizes human dexterity to create the incision, remove the lens and insert the IOL, albeit with sutureless self-sealing incisions of just a few millimetres.
Several new technologies are being used to improve outcomes in cataract surgery. These include aberrometry, laser-assisted cataract surgery multifocal IOLs, and drug delivery systems. For example, the Zeiss miLOOP reduces phaco energy, ultrasonic vibrations, surgical irrigation fluid volume and is designed for denser cataracts. The process involves a wire passed around the entire lens being retracted to slice up the lens for phacoemulsification.
Potential cataract surgery complications include posterior capsule opacity, intraocular lens dislocation and eye inflammation.
The advantages of the femtosecond laser over traditional cataract surgery is patient/surgeon based.
– Precise incisions, therefore, reducing the risk of post-operative wound leaking
– Intact capsulotomy, which can lead to a stable IOL position, is especially important for Multifocal and Trifocal IOLs. Better centration is also evident and important for patients having these types of IOL’s
– Can reduce the time spent in the eye, which is particularly important when the surgeon has capsule concerns (tears or ruptures)
– Ease of lens fragmentation during Phacoemulsification, again less time spent manipulating and pressure applied on the eye. In patients where the surgeon can predict the surgery will not be routine, the benefits of using the femtosecond laser can give positive postoperative outcomes.
DIABETES SYMPTOMS AND TREATMENT
50% of people currently living with diabetes remain undiagnosed despite the fact diabetes is a leading cause of serious health issues
Type 1 diabetes is a serious, autoimmune condition in which the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin are destroyed. Type 1 diabetes can occur at any age. Type 1 diabetes is not linked to lifestyle factors, it cannot be cured and it cannot be prevented whereas Type 2 is associated with both genetic and modifiable lifestyle risk factors.
Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition in which the body becomes resistant to the normal effects of insulin and loses the capacity to produce enough insulin. Thirty minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity on most days and a healthy diet can drastically reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.

The prevalence of diabetes has been steadily increasing for the past 3 decades, mirroring an increase in the prevalence of obesity and overweight people. In particular, the prevalence of diabetes is growing most rapidly in low- and middle-income countries.About 422 million people worldwide have diabetes
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of death in the world Complete loss of vision can occur when scar tissue develops at the back of the eye. Through the Federal Government KeepSight program, all consumers registered with diabetes on the National Diabetes Services Scheme (NDSS), will be contacted specifically to have eye and vision monitoring as part of the overall diabetes management.

A healthy diet including Omega 3s, fresh fruits and vegetables;
Take prescribed medication as directed;
Keep glycohaemoglobin (“A1c” or average blood sugar level) < 7%
Exercise regularly, control high blood pressure
Avoid alcohol and smoking.
Beware of slow-healing wounds
Seek attention for numbness in feet and hands.
Sudden blurred or double vision
Fluctuations in focusing
Eye pain or pressure
A noticeable narrowing of vision
Visible dark spots in vision or flashing lights.
excessive thirst and frequent urination
Lethargy

Heart Attack, Stroke
Peripheral Artery Disease
Diabetic Retinopathy
Cataracts
Glaucoma
Diabetic Foot
Diabetic Nephropathy (Kidney failure)
Peripheral Neuropathy (lower limb amputation)
Blindness
Gestational diabetes is a form of diabetes that can occur just during pregnancy but increases a woman’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.

Diabetic retinopathy is caused by damage to the blood vessels that nourish the retina. Vision may change accordingly.
Most people with type 1 diabetes and over 60% of people with type 2 diabetes will develop diabetic eye disease within 20 years of diagnosis.
Some warning signs and recommendations for prevention are known. Symptoms are not usually mild or absent in type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes and is diagnosed by blood glucose tests, whereas type 1 is by blood glucose and auto autoantibody testing and urine tests for ketones.

The glucose level in the blood can be measured by applying a drop of blood to a chemically treated, disposable ‘test strip, which is then inserted into an electronic blood glucose meter. The reaction between the test strip and the blood is detected by the meter and displayed in units of mg/dL or mmol/L. An insulin pump is about the size of a smartphone with thin plastic tubing and either a needle or a small tapered tube called a cannula you put under the skin.
READ MORE ABOUT DIABETES
Early diagnosis and intervention can dramatically reduce vision loss. Diabetes is the biggest challenge confronting Australia’s health system and is largely preventable. It is projected to afflict up to 10% of the population.
Higher-than-optimal levels of blood glucose increase the risk of cardiovascular and other diseases.
Type 1 diabetes is characterized by a lack of insulin production and type 2 diabetes results from the body’s ineffective use of insulin. While type 2 diabetes is potentially preventable, the causes and risk factors for type 1 diabetes remain unknown, and prevention strategies have not yet been successful. You are not born with diabetes, but rather develop it over time.
Type 2 accounts for the majority of cases of diabetes worldwide. Higher waist circumference and higher body mass index (BMI) are associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes, though the relationship may vary in different populations. Type 2 diabetes in children is increasing. There are many genetic or molecular causes of type 2 diabetes, all of which result in high blood sugar.
Possible times to check are:
Before breakfast (fasting)
Before lunch/dinner
Two hours after a meal
Before bed
Before rigorous exercise
When you are feeling unwell
The ranges will vary depending on the individual and an individual’s circumstances but target range is between 4 to 6 mmol/L (fasting).People with type 2 diabetes do not always have to take insulin right away; that is more common in people with type 1 diabetes. The longer someone has type 2 diabetes, the more likely they will require insulin.
A glycosylated haemoglobin (HbA1c) shows an average of your blood glucose level over the past 10–12 weeks. An ideal HbA1c The goal for most people with diabetes will be in the 6.5-7 percent (48-53mmol/mol) range however this may need to be higher for some people including children and the elderly.Until recently the results were shown only as a percentage. The international units (IFCC units) are shown as mmol/mol.
A blood sample taken from the vein in your arm for lab analysis or point-of-care machines where a drop of blood is taken from your fingertip and within about 10 minutes a HbA1c level can be found. Other test kits involve finger prick samples mailed to a diagnostic lab where HbA1c test results can be seen online.
Insulin can only be injected as if was tablet form would be destroyed in the stomach. Insulin is most commonly injected using an insulin pen device. Insulin can also be injected using a syringe by drawing up insulin from a vial or bottle
Insulin pumps require a catheter to be implanted every 2 or 3 days.Insulin allows the cells in the muscles, fat and liver to absorb glucose that is in the blood. The place where you put it in — your belly, buttock, or sometimes thigh — is called the infusion site. It drip-feeds insulin into the body through the day and can also deliver larger doses of insulin whenever needed, such as before meals.
As yet, there is no single genetic test to determine people are born at risk for type 2 diabetes. To develop type 2 diabetes, you must be born with the genetic traits for diabetes. Babies are rarely born with genetic neonatal diabetes. Neonatal diabetes can disappear by the time the child is 12 months of age, but diabetes usually returns later in life. We can enhance vision by supplementary glasses and electronic magnification and timely referral for laser, injections or surgery. Management includes blood glucose control through diet, physical activity, medication; control of blood pressure and lipids to reduce cardiovascular risk and other complications; and regular screening for damage to the eyes, kidneys and feet, to facilitate early treatment. The longer a person lives with undiagnosed and untreated diabetes, the worse their health outcomes are likely to be.Some people may not have any symptoms at all. In some cases, the first sign of diabetes may be a vision problem. We also use digital retinal photography and employ tests to measure the effect on vision.
