The post Covid -19 and your eye exam appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>Covid 19 symptoms can be avoided by wearing face masks. An N95 mask is ideal.

The outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 causing the disease COVID-19 was declared by the World Health Organization as a global pandemic on 11 March 2020.
Infection control by healthcare institutions is one of the key factors limiting the spread of COVID-19 and other nosocomial diseases.
The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Australian Department of Health maintain that wearing a face mask while seeing healthy, asymptomatic, low-risk patients is unnecessary. Nevertheless, wearing a medical mask is one of the prevention measures limiting the spread of certain respiratory viral diseases, including COVID-19. However, using a mask alone is insufficient to provide an adequate level of protection, and other measures should also be adopted. Patients sometimes would wear masks during testing of the visual field in automatic perimetry bowls. There has been some concern about uveitis and Covid 19 regarding the suspected adverse drug reaction of AZD1222 vaccination.
READ MORE
COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) is a novel coronavirus that is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus believed to spread from person to person via respiratory droplets. This occurs when an infected person coughs or sneezes or touches a surface with the virus present from an infected person, then touches their eyes, mouth, or nose.
Patients may be asymptomatic and infected and potentially have viral shedding for 20 days. Symptomatic patients typically present with a respiratory illness such as cough, shortness of breath and fever. Other patients may have eye pain, headaches and fatigue. The incubation period averages 5-7 days.
We are still open to looking after your eye health needs. We are taking every possible precaution to protect your health. We are sanitising all equipment each time it is used and prescreening before each patient attending to ensure that no one is displaying any symptoms associated with coronavirus.
• We use infection control methods, including face shields and goggles, P2, N95, and surgical masks, cleaning our practice, testing equipment, and consultation rooms before and after every patient use. We are being diligent with cleaning and disinfecting these areas for patient and staff safety.
• All staff are regularly using hand sanitiser and washing their hands thoroughly throughout the day. All staff are vaccinated against Covid 19
• We use the Visi2 centration system to take all our biometric measurements for spectacles, a contactless method.
• If you need to replenish contact lenses, fill solutions or collect spectacles and cannot come in, we will happily arrange for these to be posted to you.
If you have concerns about the health of your eyes and are unable to attend the practice, we can provide advice to you over the phone.
We are closely monitoring the current COVID-19 situation and following the guidelines released by both the Department of Health and Human Services and Optometry Australia to help prevent the spread of the virus.
• If you, or someone you have had close contact with, is diagnosed with COVID-19 and you have visited the practice within the last 14 days, we ask that you notify us as soon as possible to take appropriate and necessary measures. If you have any questions or concerns, please phone us on 64921999 or email us at peterdarcy.com
There is no requirement to cancel or postpone your appointment if:
• You are feeling well as we enforce social distancing and density requirements.
• HAVE NOT travelled outside Australia in the last 14 days
• HAVE NOT been in contact with any individual who has travelled outside Australia in the last 14 days.
However, courtesy to our staff and other patients, we ask that you have a cold, fever, sore throat, etc., to ring us before coming for advice.
The most common symptoms of COVID-19 are:
• fever
• flu-like symptoms such as coughing, sore throat and fatigue
• shortness of breath.
• Not everyone who has symptoms like these has COVID-19 as several other illnesses can cause these symptoms.
Fever above 38 degrees, cough, difficulty breathing, close contact, droplets
Isolate early, safety equipment, disposable tissues, hand cleaning, surface decontamination
Higher Risk Populations Some people at higher risk for developing severe illness from COVID-19 including:
• older people
• those with underlying medical problems, including high blood pressure, heart problems, diabetes, respiratory disease or immune deficiencies (low immunity).
• experience higher rates of chronic diseases than other Australians and may be at higher risk of serious illness.
What safeguards are in place if I am examined?
Patients are triaged over the phone or offered via a safe. Telehealth consultation, if appropriate.
Discretionary rescheduling of certain non-urgent appointments. Make tissues, face masks and alcohol-based hand sanitiser available in waiting areas. Perform frequent hand hygiene after contact with respiratory secretions and contaminated objects or materials
Follow respiratory hygiene techniques (i.e.. covering mouth or nose during coughing or sneezing with a medical mask, tissues or sleeve or flexed elbow, followed by hand hygiene). Immediately dispose of tissues into a hands-free waste receptacle.
Use appropriate PPE, such as surgical masks, P2/N95 masks, gloves, eye protection and breath shields for the slit-lamp
Use disposable equipment where possible. Perform systematic and enhanced decontamination of work surfaces after each patient
Staff not to attend work when unwell and also to have vaccinations as part of the employment. Encourage home delivery of spectacle/contact lenses to reduce the number of potentially infectious people visiting the practice.
Coronavirus causes and symptoms. What we can do
As well as employing Winix hospital-grade air purification, we receive daily updates from the relevant government bodies, infectious control medical experts. We are prepared and aware of the risks.
As health professionals, we have strict infection control protocols and sterilisation.
We clean all touchable surfaces between patients, including disinfecting frames after being handled.
We have all patients use our hand sanitiser upon arrival and when leaving the clinic.
If you feel unwell or have been in contact with someone who has, isolating yourself until you are all clear given the all-clear is the right thing to do!


TRISTEL DISINFECTION
Tristel Duo OPH is an approved Instrument Grade – High-Level Disinfectant.
Tristel Duo OPH is chlorine dioxide in a foam, designed specifically for the high-level disinfection of ophthalmic and optical medical devices. Tristel Duo is more compatible than alternative disinfectants such as sodium hypochlorite, aldehydes, peracetic acid or alcohol.
Tristel human healthcare products utilise chlorine dioxide for disinfection. Chlorine dioxide is a fast and effective disinfection agent activated at the point of use and does not carry many drawbacks of conventional disinfection chemistries. It has both a strong OH&S profile for staff and patients and material compatibility. The products are bactericidal, viricidal, fungicidal, mycobactericidal and sporicidal.

We use a Germidcidal lamp to sterilise frames that is powered with 253.7 nm UV rays that quickly remove every single micro-organism. The treatment does not generate heat. Frames and tools once sterilized can be kept for a long time, enabling them to be stored and ready for use.
The inside shelf keeps the items away from the reflecting surface in order that the rays uniformly coat the products, so as to optomise germicidal action.
For a better result we do not place items on top of each other. For frames with ophthalmic and special treatment lenses we remove the lenses first as
continuous treatment can cause the lenses to yellow. Sterilization time:
From 60 seconds to a maximum 90 seconds.
READ MORE
For devices that contact the surface of the eye or secretions, Tristel Duo OPH is used as is TGA approved specifically for high-level disinfection of small devices such as tonometer prisms and gonioscope lenses, pachymeters, ultrasound A- and B-scanners, etc.
For all clinic surfaces (whether treatment room, medical surfaces such as headrests, reception desks or cabinetry), Tristel Jet Gel is effective against all organisms of concern in 30-seconds of contact.
EFFICACY AND SAFETY COMPARISON TRISTEL DUO OPH AND 70% IPA
Hazard Statements DUO OPH has no hazardous classifications according to CLP, whereas IPA is a highly flammable liquid and vapour and can cause serious eye irritation, drowsiness and dizziness.
| TRISTEL DUO OPH | 70% IPA | |
| Gram-negative bacteria (e.g. Pseudomonas aeruginosa) |
30 secs | 5 mins |
| Gram-positive bacteria (e.g. Staphylococcus aureus) |
30 secs | 5mins |
| Yeast (e.g. Candida albicans) |
30secs | 5mins |
| Fungi (e.g. Aspergillus brasiliensis) |
30 secs | 5mins |
| Viruses (e.g. Adenovirus, Herpes simplex virus) |
30 secs | NA |
| Mycobacteria (e.g. Mycobacterium terrae) |
2 mins | NA |
| Bacterial spores (e.g. Clostridium sporogenes) |
2 mins | NA |
Duo Wipes are low-linting, non-scratching, and non-absorbent. This means they apply the chemistry effectively and efficiently (rather than absorbing it) and leave surfaces pristine and clean.
Studies comparing the ‘absolute risk’ of viral infection or transmission for people with eye protection – such as a face shield or goggles – compared to those without – found those with no eye protection faced a 16% likelihood of contracting the virus. In comparison, those adopting the protective measure reduced their chances to 5.5%, equating to a 10.5% difference or a 3x decrease in risk.
What safeguards are in place if I am examined?
Patients are triaged over the phone or offered via a safe. Telehealth consultation, if appropriate.
Discretionary rescheduling of certain non-urgent appointments. Make tissues, face masks and alcohol-based hand sanitiser available in waiting areas. Perform frequent hand hygiene after contact with respiratory secretions and contaminated objects or materials
Follow respiratory hygiene techniques (i.e.. covering mouth or nose during coughing or sneezing with a medical mask, tissues or sleeve or flexed elbow, followed by hand hygiene). Immediately dispose of tissues into a hands-free waste receptacle.
Use appropriate PPE, such as surgical masks, P2/N95 masks, gloves, eye protection and breath shields for the slit-lamp
Use disposable equipment where possible. Perform systematic and enhanced decontamination of work surfaces after each patient
Staff not to attend work when unwell and also to have vaccinations as part of the employment. Encourage home delivery of spectacle/contact lenses to reduce the number of potentially infectious people visiting the practice.
COVID-19: Background
• Coronaviruses are a family of viruses that can make humans sick
• The new coronavirus disease, officially known as COVID-19, originated in China in 2019 and has since spread around the world
• Most people, around 80% who become infected with COVID-19, will experience only mild symptoms and fully recover without any special treatment
• Some people, around 15% of those who become infected with COVID-19, will experience moderate symptoms
• A small number of people who become infected with COVID-19, approximately 5%, may experience severe symptoms and get very sick
• It is important to know how to protect yourself, your family and your community
Protecting yourself and others in the workplace
You can help keep yourself and others safe by practising good infection and prevention and control in your workplace.
You can use the same principles at work and home:
Clean your hands regularly
Practice social distancing
Practice respiratory etiquette Practical tips for protecting yourself and others in the workplace
Put marks on the floor to ensure customers stand at least 1.5 metres away from the counter and each other.
Practise hand hygiene between customers
If you are in an open plan office
Make sure there is at least 1.5 metres between yourself and the next workstation.
READ MORE
Social Distancing
• Maintain at least 1.5 metres distance between yourself and anyone who is coughing or sneezing
• This is important because if you are too close to someone, you might breathe in droplets they cough or sneeze
Use good respiratory hygiene.
• Make sure you and the people around you follow good respiratory hygiene.
- This means covering your mouth and nose when you cough and/or sneeze with:
You put a tissue you put in the bin straight after use, your bent elbow, and maintain social distancing. - Respiratory hygiene is important because droplets spread the virus. By following good respiratory hygiene, you ‘catch’ any droplets that might be produced, and this protects the people around you from viruses, including COVID-19.
Remind those in your care to use good respiratory hygiene
Make sure that when you are out and about, you carry tissues for yourself and others to use
Remind those in your care to clean their hands after coughing or sneezing
• If you are further away than 1.5 metres, it is improbable that you will breathe in droplets that might contain COVID-19
• Help those that you care for by keeping 1.5 metres between themselves and others
• This is especially important if you’re out and about
• Avoid large public gatherings, unless essential
• Remember that COVID-19 can be transmitted by droplets that can be passed from hand to hand, including handshakes
- Centres for disease control and prevention advise the n95 mask with ear loops to protect the wearer. Disposable masks can be utilised depending upon the respiratory need.
- Click here to see how vaccines work.
- Australia has secured 10 million doses of the Pfizer vaccine and 53.8 million of the AstraZeneca vaccine produced onshore by CSL in Victoria.
People will need two doses of the Pfizer vaccine, meaning it will cover five million Australians when it is distributed.
The World Health Organization (WHO) stipulates the doses should be given within 21 to 28 days.
Food Safety
• From the information we know at present, COVID-19 doesn’t seem to be spread by food
• However, you should still make sure you prepare food safely to make sure that you and others don’t get sick from other diseases
• This is important when you are preparing food for yourself and those in your care, washing hands between handling raw and cooked foods
• using different chopping boards for raw meats and cooked foods, ensuring all meats are cooked thoroughly. When you are preparing food, you should always practise good respiratory etiquette, and if you have symptoms of a respiratory illness, you should avoid preparing food for other people.
Managing visitors
• Keeping safe from COVID-19 does not mean having any social life for yourself or those in your care
• It is important to maintain relationships
• People who are unwell should be advised to stay in their own homes and not visit others
• This is particularly important to enforce in residential settings where people should stay in their own room
• Visitors to residential facilities should be encouraged to wash their hands on entering and exiting the facility and before and after visiting any resident
Taking people in your care out in public
• Regular hand hygiene, social distancing, and respiratory etiquette are essential in public settings
• Practice hand hygiene after touching shared surfaces (e.g. in shops, cafes or on public transport)
• To maintain social distancing, you should avoid large public gatherings unless essential
Protecting yourself and others in the workplace
- You can help keep yourself and others safe by practising good infection and prevention and control in your workplace.
- You can use the same principles at work and home:
- Clean your hands regularly
- Practice social distancing
- Practice respiratory etiquette Practical tips for protecting yourself and others in the workplace
- Put marks on the floor to ensure customers stand at least 1.5 metres away from the counter and each other.
- Practise hand hygiene between customers
- If you are in an open plan office
- Make sure there is at least 1.5 metres between yourself and the next workstation.
- Have meetings in large enough rooms for everyone to sit 1.5 metres apart (mark the desks with tape)
- Ensure you wipe down surfaces in your work area regularly
- If you are doing household deliveries:
- If possible, avoid face to face contact with those inside the house, e.g. leave goods at the front door and call the house occupants to let them know their delivery has arrived.
- If you need to have face to face contact with those inside the house, then stand at least 1.5 metres back from the door when it is answered.
- Practice hand hygiene when you get back in the car after every delivery
- Wipe down surfaces in your car (including the steering wheel and door handles) regularly
- Practice regular hand hygiene
- Practice social distancing
- Practice respiratory etiquette
- Seek medical advice, remember to call first, and inform your workplace if you have symptoms. Keep yourself and others safe.
- Remember, whilst COVID-19 can seem scary, you can help stop it from spreading and protect yourself and those in your care.
- Most importantly, wash your hands and make sure those in your care do the same.
- Practice respiratory etiquette and make sure those in your care do the same
- Practice social distancing and make sure those in your care do the same

Masks and Covoid-19
Those who are sick should wear a mask if they went out. (Ideally, however, those who are sick should stay at home and those confirmed to have COVID-19 should be isolated and cared for in a health facility and their contacts quarantined).
Home caregivers should wear a mask to protect themselves and prevent further transmission.
Health workers should wear medical masks and use other protective equipment when dealing with suspected or confirmed COVID-19 patients.
READ MORE
Wearing a facemask in public won’t help to protect you from infection
• Only wear a mask if you are sick with symptoms that might be due to COVID-19 (especially coughing) or looking after someone who may have COVID-19
• There is a shortage of masks and we need to save them for use when they are needed for sick people or those looking after them
• Remember the best ways to protect yourself and others against COVID-19 are: Regularly wash your hands, Use respiratory etiquette to catch your cough or sneeze
In areas with the widespread transmission, medical masks for all people working in clinical areas of a health facility should be worn. In areas with community transmission, members of the general public aged 60 and older and those with underlying conditions should wear a medical mask when physical distancing is not possible. The general public should wear non-medical masks where there is widespread transmission and when physical distancing is difficult, such as on public transport, shops, or other confined or crowded environments.
Cloth masks should consist of at least three layers of different materials: an inner layer being an absorbent material like cotton, a middle layer of non-woven materials such as polypropylene (for the filter) and an outer layer, which is a non-absorbent material such as a polyester or a polyester blend. Masks sometimes can create mask associated with dry eye.
Fogging happens because of the phase change of matter. Water vapour (from exhaled breath and sweat from your forehead) cools down when it touches the lenses. The cold lenses cause a phase change as the warm vapour touches them and turns into a liquid. There is a controlled temperature that each coating is based on. This means there is an optimum temp that the coating will work at, and as the temp gets further away from his, the less likely to work efficiently.
Ant Fog cloths and sprays work by placing another layer over the lens, which in time will wear off! This is also temperature dependant. Most products designed with face masks, so they would work more for steam/ heat. This means the fogging you get on a cold morning putting on your glasses may still occur depending upon the treatment. Airflow between the lens and the wearers face is a major determinant in the fogging factor.
Travel and COVID-19
• Currently, many cases of coronavirus in Australia are imported from overseas
• Therefore, if you are a frontline healthcare worker, carer, volunteer or have close contact with high-risk persons and you have recently travelled overseas, you may be asked to stay away from work for a certain period after your return
READ MORE ABOUT TRAVEL AND COVID 19
What if I develop symptoms of COVID-19?
If you develop symptoms such as fever, dry cough, sore throat, and fatigue, you should:
stay at home and practice standard infection control precautions
seek medical advice; it is important to call ahead first:
go to www.healthdirect.gov.au; or
Call the National Coronavirus Information and Triage Line (1800 020 080); or
Call your usual care provider and inform your workplace. What if someone in my care develops symptoms of COVID-19?
If someone in your care has symptoms of COVID-19, you should:
Keep them at home, or if they are in a group facility, keep them isolated in their own room
Ensure they practice standard infection control precautions and seek medical advice promptly; remember to call ahead first.
If someone in your care is suspected by a medical professional as having COVID-19, then you will need to practice further infection control measures, including the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE)
You will need to seek further advice on this from your local public health unit or infection control specialist key messages for COVID-19.
You can help protect yourself, your family, your workplace and your community.
Stay informed on the latest developments about COVID-19. Click here for Up to date information at https://www.health.gov.au/news/health-alerts/novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov-health-alert.
Monitor news updates regarding local events and gatherings
Follow current advice given by your national and local public health authorities.
1-3% of patients with COVID may have some form of red-eye/conjunctivitis. The actual risk of transmission through tears is considered quite low; however, the discovery of viral RNA in infected patients means avoiding aerosol-generating procedures and following triaging, disinfection and appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) practices. Those who recover from Covid may have an increased risk of strokes, lung damage, heart damage, blood clots, which is more serious in the elderly. In contrast, polio in the past had similar mortality rates that affected more of the youth.
Cleaning and disinfection
• Regular cleaning of your environment, at home, in your car and at work is essential
• This is because droplets from an infected person can fall on a surface, and be transferred to
someone else’s hands if they touch the surface
• You should regularly clean frequently touched surfaces, for example, tables, doorknobs, light switches
• To clean use a detergent solution according to the manufacturer’s label, preferably Tristel products to disinfect.
• Remember to check the product label for any precautions you should take when using it, such as wearing gloves or making sure you have good ventilation
READ MORE ABOUT CLEANING AND DISINFECTION
NHRMC Feb 2020 Infection control guidelines state ultra-violet light in the UV-C wavelength range (200 to 270 nanometers) has microbiocidal properties against multiple pathogens. The International Commission on Illumination (Commission Internationale de l´Eclairage ) is the authority on all matters relating to the science and art of light and lighting, colour and vision, photobiology and image technology.
While UV-C is extremely useful in the disinfection of air and surfaces ( the 200-220nm range is effective against viruses and bacteria and is safe to be used without causing damage to human tissue cells/mammalian skin, longer wavelengths may cause skin cancer and cataracts ) or sterilization of water, the CIE and the World Health Organisation (WHO) warn against the use of UV disinfection lamps to disinfect hands or any other area of skin.
There is insufficient evidence-based data on its use. UV deactivation of COVOID only occurs with the correct dose, exposure time and wavelength, and by clean nonshadowed or non obstructed contact. UV-C can be very hazardous to humans and animals and should only be used in carefully controlled circumstances. UV-C can cause photodegradation of materials and this should be considered where susceptible materials, such as plastics, are in the exposed environment.
Tristel is the only Medical grade disinfectant that is TGA approved, and suitable.
Surface disinfection options
– Ask patients to use hand sanitiser before entering the practice
– Follow social distancing and encourage patients to remain 1.5m from the desk
– Desks clear of clutter
– EFTPOS terminals with an appropriate disinfectant between patients and encourage contactless payments over cash
– Minimise patient use of pens, and sanitise before and after use
– The daily log kept of patients/people in practice in case contact tracing needs to occur
– Wipe down of all surfaces (door handles, tabletops, light switches, chairs) and desks
– Removal of all flowers, tea/coffee facilities and toys
– Tissues and face masks are readily available
Sodium hypochlorite is often used in “at home” situations
Clean with mild pH neutral detergent or soap
Rinse with sterile water/saline before disinfecting
Soak in sodium hypochlorite (5000ppm) for 10 minutes
Rinse with sterile water/saline
Air dry or dry with a sterile, soft disposable cloth. Note: The appropriate concentration of sodium hypochlorite is 5000ppm, approximately 0.5%. Household bleach is 5-6% sodium hypochlorite, so a 1:10 dilution of bleach (1 part bleach, 9 parts water) equals 5000ppm.
Contact lens disinfection protocols
A review of the evidence, published in July’s Clinical and Experimental Optometry, indicates the eye is an unlikely site for SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. However, ocular manifestations such as conjunctivitis and the presence of SARS‐CoV‐2 in tears had so far only been found rarely in people with confirmed, symptomatic COVID‐19.
READ MORE ABOUT CONTACT LENS DISINFECTION
All cases of keratoconjunctivitis, especially those with associated upper respiratory tract symptoms, however mild, should be considered as potential COVID‐19 cases.
Scrupulous contact lens hygiene practices should continue to be advocated, along with the use of correct wear, care, cleaning and replacement of lenses and lens cases, given the need for contact lens wearers to touch their face and eyes on application and removal.
Cleaning Rub with a daily surfactant cleaner for RGP lenses or multipurpose solution (MPS) for soft and hybrid lenses. Rinsing Rinse with sterile saline or MPS for at least 30 seconds
Inspection Inspect the lens for damage/defect and dispose of it appropriately if necessary. Preparation Fill a non-neutralising CL case with 3% hydrogen peroxide.
Disinfection Soak lens for at least 3 hours without neutralising Neutralisation For soft and hybrid lenses, refill a neutralising case with fresh hydrogen peroxide and add neutralising tablet/disk. Soak for recommended neutralisation time (e.g. 6 hours)
Rinsing Rinse with sterile saline (or MPS). Storing Store RGP lens dry after wiping with a clean, lint-free tissue. Use disinfected tweezers to store the soft or hybrid lens in MPS. For soft or hybrid lenses, it is recommended to repeat the full disinfection process every 28 days.
Soft contact lenses can also be sterilised in an autoclave at 134°C for at least 3 minutes or 121°C for at least 10 minutes.
The post Covid -19 and your eye exam appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>The post Migraines and Eyes appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>
WHAT IS A MIGRAINE?
Migraine headaches, sometimes preceded by warning symptoms, can have specific triggers but also can vary in severity and type.
As distinct from the tight band type tension headache and the cluster headache often around one eye, the classic migraine is on one side of the head with the vision effected. Migraine is a common headache disorder with no conclusive cures, of many types affecting about 15 per cent of the population, but much is underdiagnosed and can have serious health risk warnings eg women suffering from migraine with aura at any age should never use oral contraceptives accordingly.
A diagnosis of migraine is one of exclusion. especially in recent onset cases, increasing severity/frequency, neurological symptoms of pins and needles and visual field defects all indicate further work up is indicated eg MRI with a neurologist or neuro-ophthalmologist
Migraine can be triggered by many factors such as food, medication,weather, stress, lack of sleep, skipping meals, dehydration. Triggers need to be kept in a diary,ideally.
WHAT CAUSES MIGRAINES ?

WHAT CAUSES MIGRAINE PAIN ?
Researchers have identified more than 20 irregular chromosome segments associated with migraine. Each potential genetic error affects how nerve cells work in a different way. The most effective treatments control the individuals triggers for migraines often called predisposing and precipitaing factors.
The brainstem is a complex intersection of nervous system wiring at the base of our brain in clusters of cell bodies called nuclei. From these nuclei, new signals are rerouted to other parts of the brainstem and the rest of the brain.These nuclei control pain, stress, balance, mood, sleep and the autonomic nervous system.
MEDICAL FILTERS
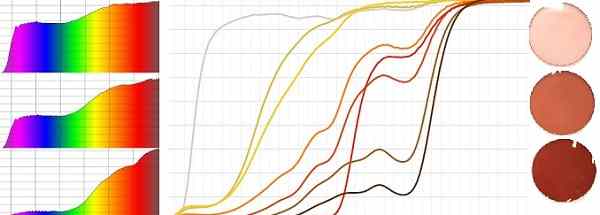
The FL-41 tint has been used successfully for migraine sufferers and in certain neurological conditions.
READ MORE
At 75% luminous transmittance or 25% absorption as an over the counter sunglass category 2 (43% to 80% luminous transmittance) it would have to be marked
“Not suitable for driving at twilight or night” or “Not suitable for drivng at night or under conditions of dull light”
Traffic signal visibility requirement must also be met for OTC and prescription. If they don’t then they must be marked “Notsuitable for driving and road use”
If they are considered precription, then AS/NZS ISO 8980-3 applies,
6.3.4 Driving in twilight or at night refers spectacle lenses with a luminous transmittance less than 75% shall not be used for driving in twilight or at night.
Medical filters are dyed according to the transmission curve
MEDICAL FILTER LENSES can be used for
• Age-related macular degeneration
• Albinism
• Diabetic retinopathy
• Retinitis pigmentosa
• Achromatopsia (colour blindness) Migraines
• Cone-rod-dystrophy
• Iris coloboma
• UV protection for pseudophakia and aphakia
• Photochemotherapy,
Medical filter lenses absorb short-wave blue light components more strongly than conventional sun protection lenses or contrast-enhancing lenses. Medical filters lenses can restrict peripheral vision due to the (almost) complete absorption of short-wave blue and violet light – which is extremely important in sports.
The short-wave violet and blue light causes scattering in the eye, which leads to glare and a reduction in acuteness of vision.
The contrast is increased by the difference between the strongly and less strongly exposed receptors.
Visual symptoms such as blurred vision, visual aura and photophobia can occur during migraine attacks, but not necessarily always.
Less than half of current migraine sufferers have been formally diagnosed, and about one-third are thought to receive appropriate treatment with prescription medications.
Colourimeter research data determines certain specific tints can help migraine sufferers whose migraines are triggered by pattern glare.
BPI manufactures the pink FL-41 dye is a mixture of colours that blocks the blue-green wavelengths.
BPI is the world’s largest manufacturer of optical tints.
Though the efficacy of Blue Light Blockers can vary, environmental exposure to blue light, including those from digital screen technology, does not cause significant damage to eyesight. Therefore, filtering out the blue light from screens is not essential but can be helpful.
The FL-41 tints in 25, 50 and 75% transmissions. (The % related to how dark the tint saturation is.) are sometimes prescribed for patients with migraine or brain trauma.
Research shows that there is not one specific colour to treat migraine (or any condition) as peoples vision and brains react differently and need to be treated individually. This is the reason the Colorimeter has 110,000 different colour combinations.
Pattern glare tests involve tints (that later can be prescribed) often but not always blue or yellow to reduce nausea that can arise from stripe patterns for some people by reducing or changing the contrast between black and white.
The theory is some people have a hyperactivity imbalance between their central and peripheral vision for light, flicker and specific spatial frequencies in stripes and patterns and can make reading difficult.
Optometrists do not treat “dyslexia” or even learning difficulties, but learning-related vision problems, and in the above cases treat people with pattern glare with tints when it affects reading.
Migraine is a complex and the most common neurological condition and classified by the World Health Organisation as the 7th most disabling disease worldwide, the 4th for women. It is three times more common in women than it is in men and is usually inherited. It is a very individual condition. Some people experience only an odd attack, while others suffer them regularly
TYPES OF MIGRAINES
RETINAL MIGRAINE
A retinal migraine (aka ophthalmic, migraine, visual, ocular ) has the temporary loss of vision effect by definition. (A headache that lasts from 4 -72 hours.)
An aura usually appears in both eyes.
Retinal migraines involve episodes of temporary vision loss or blindness in one eye only.
A retinal migraine often comes on suddenly in concert with head pain and nausea from a vascular spasm in or behind an eye.
Retinal migraines are apparent in 1 in 200 migraine sufferers with short-term loss of vision in one eye only.
• flashing lights or haloes
• blind spots in your field of vision
• partial or complete blindness
• affect one side of the head
•painful
• aggravated by activity
• nausea and vomiting
• sensitivity to light/sound
MIGRAINE WITH AURA
Aura :
Blind spots
Flashing lights
Zig-zag patterns
Pins and needles on one side usually starting in the fingers/ arm, sometimes spreading up into the face.
Slurring of speech
Muscular weakness
Loss of co-ordination
Confusion) up to an hour duration can occur in about 20% of cases before the actual headache.
The actual headache:
Intense throbbing headache, usually on one side of the head, worsened by movement and lasting from 4-72 hours.
Nausea, sometimes vomiting.
Sensitivity to light, noise, smells, Stiffness of the neck and shoulders, Blurred vision.
MIGRAINE WITHOUT AURA
Most commonly, migraine occurs without the aura but with the headache
The intense throbbing headache, usually on one side of the head, worsened by movement and lasting from 4-72 hours.
Nausea, sometimes vomiting
Sensitivity to light, noise, smells
Stiffness of the neck and shoulders.
Blurred vision
MIGRAINE WITHOUT HEADACHE
Occasionally migraineurs can experience only the aura of
Blind spots
Flashing lights
Zig-zag patterns
Pins and needles on one side usually starting in the fingers/ arm, sometimes spreading up into the face.
Slurring of speech
Muscular weakness
Loss of co-ordination
Confusion
OPTHALMOPLEGIC
As well as the headache occurring mainly in young people, there is the weakness of one or more of the muscles that move the eye, dilate the pupil and control the eyelids.
BASILAR
Rarely in young women, mainly loss of balance, double vision, blurred vision, difficulty in speaking and fainting.
Headache, loss of consciousness. Basilar migraine occurs when the circulation in the back of the brain or neck is affected.
HEMIPLEGIC
It is rarely headache but with temporary numbness, weakness, or even paralysis on one side of their body up to a few days in duration.
MRIs, CT scans and other neurological tests are required to rule out stroke, blood clot stroke, pituitary tumour, detached retina, or drug abuse.
Treatment causes etc
Acute medications used include the normal NSAIDs such as Ibuprofen,anti-nausea medication as well as preventative medications.
VESTIBULAR
Many migraine sufferers experience some vestibular symptoms during their lifetime, such as dizziness, sensitivity to light/sound and stiffness of the neck
but severe vestibular migraine can encompass
Severe dizziness
Vertigo
Sensitivity to light, sound, smell
Nausea and vomiting
Ataxia (loss of control over bodily movement)
Neck pain
Muscle spasms in the upper spine area
Confusion
At 75% luminous transmittance or 25% absorption as an over the counter sunglass category 2 (43% to 80% luminous transmittance) it would have to be marked
“Not suitable for driving at twilight or night” or “Not suitable for drivng at night or under conditions of dull light”
Traffic signal visibility requirement must also be met for OTC and prescription. If they don’t then they must be marked “Notsuitable for driving and road use”
If they are considered precription, then AS/NZS ISO 8980-3 applies,
6.3.4 Driving in twilight or at night refers spectacle lenses with a luminous transmittance less than 75% shall not be used for driving in twilight or at night.
Medical filters are dyed according to the transmission curve
MEDICAL FILTER LENSES can be used for
• Age-related macular degeneration
• Albinism
• Diabetic retinopathy
• Retinitis pigmentosa
• Achromatopsia (colour blindness) Migraines
• Cone-rod-dystrophy
• Iris coloboma
• UV protection for pseudophakia and aphakia
• Photochemotherapy,
Medical filter lenses absorb short-wave blue light components more strongly than conventional sun protection lenses or contrast-enhancing lenses. Medical filters lenses can restrict peripheral vision due to the (almost) complete absorption of short-wave blue and violet light – which is extremely important in sports.
The short-wave violet and blue light causes scattering in the eye, which leads to glare and a reduction in acuteness of vision.
The contrast is increased by the difference between the strongly and less strongly exposed receptors.
Visual symptoms such as blurred vision, visual aura and photophobia can occur during migraine attacks, but not necessarily always.
Less than half of current migraine sufferers have been formally diagnosed, and about one-third are thought to receive appropriate treatment with prescription medications.
Colourimeter research data determines certain specific tints can help migraine sufferers whose migraines are triggered by pattern glare.
BPI manufactures the pink FL-41 dye is a mixture of colours that blocks the blue-green wavelengths.
BPI is the world’s largest manufacturer of optical tints.
Though the efficacy of Blue Light Blockers can vary, environmental exposure to blue light, including those from digital screen technology, does not cause significant damage to eyesight. Therefore, filtering out the blue light from screens is not essential but can be helpful.
The FL-41 tints in 25, 50 and 75% transmissions. (The % related to how dark the tint saturation is.) are sometimes prescribed for patients with migraine or brain trauma.
Research shows that there is not one specific colour to treat migraine (or any condition) as peoples vision and brains react differently and need to be treated individually. This is the reason the Colorimeter has 110,000 different colour combinations.
Pattern glare tests involve tints (that later can be prescribed) often but not always blue or yellow to reduce nausea that can arise from stripe patterns for some people by reducing or changing the contrast between black and white.
The theory is some people have a hyperactivity imbalance between their central and peripheral vision for light, flicker and specific spatial frequencies in stripes and patterns and can make reading difficult.
Optometrists do not treat “dyslexia” or even learning difficulties, but learning-related vision problems, and in the above cases treat people with pattern glare with tints when it affects reading.
Migraine is a complex and the most common neurological condition and classified by the World Health Organisation as the 7th most disabling disease worldwide, the 4th for women. It is three times more common in women than it is in men and is usually inherited. It is a very individual condition. Some people experience only an odd attack, while others suffer them regularly
The post Migraines and Eyes appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>equipment,eyedrops can all be required
The post Fire and Eye Protection appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>
TYPES OF FIRE GOGGLES
Let us help you with your specific needs.
The human eye is susceptible to damage and needs the correct protection and comfort, particularly in fire hazards from simple eye drop to specific eyewear and goggles/face shields.
Some goggles are single-piece lenses that can be fitted over glasses.
Slimline versions often have a two-piece lens design and are more comfortable when used under helmets.
Some goggles tested to AS1337 can be both stand-alone or attached to an AS1801 Certified bushfire helmet.
TYPES OF RESPIRATORS FOR FIRE FIGHTING
Disposable active carbon respirators reduce smoke & chemicals more than standard disposable respirators.
Types of respirators are also classified by the type of hazard they protect against.
Negative-Pressure Negative-pressure respirators rely on the wearer to pull air in through cartridges or filters.
Filtering Facepiece Disposable respirators, also known as filtering facepieces, help protect against some particulate hazards.
Reusable respirators Reusable types can be used with particulate filters, gas and vapour cartridges or combination cartridges.
Half-face respirators Half face types cover the lower half of the face, including the nose and mouth.
Full-Face respirators Full-face respirators cover the eyes and much of the face and sometimes replace the need for safety glasses.
Positive Pressure respirators do the work of pushing air to the respirator head top or facepiece.
Tight Fit respirators
Loose-fitting respirators typically have a hood or helmet.
Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus.
DON’T FORGET THE CORRECT EYE DROPS, FILTERS, FIRE SAFETY EYEWEAR, AND ANTIFOG WIPES.
READ MORE ABOUT PARTICULATE FILTERS
There are different types of particulate filters and gas and vapour cartridges.
As per AS/NZS 1715, there are 3 different particulate filters, P1, P2, and P3.
The negative pressure particulate categories are based on facepiece coverage. All particulate filtering facepieces covering the nose and mouth area can only achieve a P1 or P2 classification. A P3 classification can ONLY be achieved when worn with a full facepiece.
Class P1 particulate filters are used against mechanically generated particulates, e.g. silica and wood dust.
Class P2 particulate filters are used for protection against mechanically and thermally generated particulates or both.
P2 Respiration Mask is intended for use against bushfire smoke, metal fumes, lead, silica & coal dust, asbestos fibre, bacteria, fungi, + more. Great to keep at home or in the car in case of a bushfire.
Class P3 particulate filters are used for protection against highly toxic or highly irritant particulates, e.g. beryllium (when worn with a full facepiece). Certain contaminants may have specific respiratory selection criteria.
Their filter type and class distinguish gas and vapour cartridges categories. Some commonly used filter types are:
Filter type A = Certain organic vapours (boiling point above 65⁰C) from solvents such as those in paints and thinners (cartridge label colour = brown)
Filter type B = Acid gases such as chlorine, hydrogen sulphide (sulphide) and sulphur dioxide (cartridge label colour = grey)
Filter type E = Vapours from sulfur dioxide (cartridge colour = yellow)
Filter type ABE = are suitable for both certain organic vapours/acid gases and sulphur dioxide, e.g. solvents, chlorine and sulphur dioxide (cartridge label colour = brown, grey and yellow)
Filter type K = ammonia gas (cartridge label colour = green)
Filter type ABEK = are suitable for both certain organic vapours/acid gases, sulphur dioxide and ammonia (cartridge label colour = brown, grey, yellow and green)
READ MORE ABOUIT ASTHMA AND SMOKE
Government Health agencies report air quality for PM2.5/PM10 levels.
SMS alerts can be organised, e.g. for asthmatics who can be breathless or wheezy or have a tight chest or persistent cough exacerbated by smoke.
So as using a reliever (for example, Ventolin), preventer medication could be used while air quality remained poor.
The anti-inflammatory action of corticosteroids makes them an effective anti-asthma treatment. An example of inhaled corticosteroids is budesonide (e.g. Pulmicort);
Sometimes combined with a long-acting beta2 agonist (to help keep the airways open for up to 12 hours) such as Seretide (fluticasone plus salmeterol);
Drugs that block leukotrienes, which cause narrowing and swelling of the airways, can also improve asthma symptoms and help prevent asthma attacks, e.g. Lukair tablets.
Chrome medicines, such as sodium cromoglycate (e.g. Intal)and nedocromil sodium (e.g. Tilade), are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory asthma medications.
The higher the Air Quality Index (AQI value scaled from 0-500), the greater the level of air pollution and potential issues. This measure of fine particles in the air less than 2.5 micrometres of between 300-500+ is considered hazardous. Adverse effects include aggravation to the heart and lungs among the general public – particularly for sensitive groups, including children, the elderly, those suffering from cardiac or pulmonary diseases and pregnant women.
Avoid exposure to the smoke by staying indoors where possible and not using evaporative airconditioners, which draw air into the house from outside.
If the exterior smoke and air quality are inferior, windows, doors and entry holes need to be shut to prevent smoke entry.
Air purifiers fitted with PM 2.5 particle filtering are designed to capture pollutants and particles but emitting the filtered air. Evaporative coolers can be used if the system is filtered, and air conditioners that have switches to ‘recycle’ or ‘recirculate’ can reduce the amount of smoke entering the premises. Air conditioners without controls can run in fan mode instead of cooling and need to have their filters cleaned regularly.
Asthmatics need to avoid dust mites, harsh cleaning chemicals, hairspray, smoke, non-flued gas heaters and wood-burning fires.
Eye conditions such as dry eye, blepharitis or allergic conjunctivitis are exacerbated by the burning and stinging eye pain that smoke, noxious gases, embers can cause but lubricating the eyes with the correct type of eye drops can sometimes be useful. Smoke from vegetation is composed of hundreds of chemicals in gaseous, liquid and solid forms. These include toxic gases (e.g. carbon monoxide), aldehydes, benzene, water vapour and small particles of carbon and other materials (median aerodynamic equivalent diameter of 3.5µm).
Exposure to these substances (mainly carbon monoxide and aldehydes) and gases or particles from plastics or rubbers can cause eye irritation and injury.
Common symptoms following exposure to and contact with smoke include pain, discomfort, redness, and watering of the eyes.
Other possible injuries resulting from exposure to fires and smoke include corneal abrasions, conjunctivitis burns to the eyelids, eyeball, and face.
Be careful NOT to rub your eyes which can worsen the irritation and reduce contact lens wear.
Cooling compresses over your eyes can be soothing, and try to maintain a more humid indoor environment. Specialty goggles that are often prescribed to patients with dry eyes can be an effective option for people experiencing sensitivity to smoke in the air. And close-fitting glasses or sunglasses will provide at least some barrier to particle pollution.
More specific treatment can result after careful examination.
The post Fire and Eye Protection appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>The post Macular Degeneration Supplements appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>Nutritional supplements play a role in slowing the progression of dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD) to late-stage AMD.

MDeyes delivers the complete AREDS 2 proven low zinc formula, including the specific quality ingredients FloraGLO Lutein and OPTISHARP Zeaxanthin, in a convenient once-daily capsule. The packaging helps with compliance by calendar labelling on the blister foils.

AREDS antioxidant supplements remain the most proven way of slowing progression to late-stage AMD in high-risk patients. MDeyes is Australia’s most affordable AREDS 2 capsule formula at $20.95 (RRP).

The benefit of AREDS2 antioxidant supplements in dry cases extends by not smoking and performing light exercise, and increasing dietary intake of omega-3 and carotenoids. Ideally, a ‘Mediterranean diet, rich in fish, nuts, vegetables, fruit, and legumes, has been associated with lower AMD incidences.
READ MORE ABOUT MACULAR SUPPLEMENTS
The MDeyes powder option mixes easily with water to avoid capsules, includes FloraGLO Lutein and OPTISHARP Zeaxanthin. No added gluten, dairy, sodium potassium salts, wheat, lactose, colours, flavours, preservatives. Has a great-tasting natural orange flavour with no artificial colours, flavours or added sugar. Includes a 4g scoop for dosage compliance and has $29.95 (RRP) per tub (40 serves)
In wet cases of ARM (leakage of microvessels), anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) injection may help. Whereas there are potential benefits of antioxidant supplements in cases of dry ARM
The exact mechanism by which this process occurs is not fully known. Age, genetics, and exposure to both endogenous and environmental oxidative stress are factors.
The original AREDS formula (2001) involved a randomised, multicentre, double-masked and placebo-controlled clinical trial of 4,757 patients. OVER SUBSEQUENT YEARS, the AREDS study’s follow-up results showed much data in reducing vision loss using AREDS had proven antioxidants.
A further AREDS2 Research Group followed 4,203 patients. It showed, particularly in patients with a history of smoking and/or a low dietary intake of lutein and zeaxanthin, that an improved formula could be used. Also, beta-carotene was removed as well as using a lower dose of zinc.
Of the hundreds of carotenoids in normal diets, only lutein and zeaxanthin are naturally concentrated within the macula. They provide antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties and short-wavelength blue light protection.
Accordingly, an increased dietary intake of lutein and zeaxanthin may be protective against the development of late AMD but not early AMD. Omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids and other particular acids have also been studied trying to improve the formula.
The post Macular Degeneration Supplements appeared first on Peter D'Arcy Optometrist.
]]>